Social anxiety is not just about feeling a little shy at parties. For many, it’s a profound fear of social situations, a debilitating apprehension of being judged, criticized, or simply being around others. While everyone might feel nervous or out of place from time to time, individuals with social anxiety experience these emotions at a much deeper level. This blog aims to shed light on the intricacies of social anxiety, and how social anxiety counseling is helpful in the pathways to resilience.
Contents
Understanding Social Anxiety
 Social anxiety, often referred to as Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), is more than just the occasional nervousness one might feel before giving a speech or attending a large gathering. It is a persistent and often overwhelming fear of social interactions. It is driven by the intense worry of being negatively judged or scrutinized by others. This fear can manifest in various social situations, from ordering food at a restaurant, making small talk with a neighbor, to even just the thought of being around other people.
Social anxiety, often referred to as Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), is more than just the occasional nervousness one might feel before giving a speech or attending a large gathering. It is a persistent and often overwhelming fear of social interactions. It is driven by the intense worry of being negatively judged or scrutinized by others. This fear can manifest in various social situations, from ordering food at a restaurant, making small talk with a neighbor, to even just the thought of being around other people.
While everyone can feel shy or uncertain in unfamiliar social situations, what sets social anxiety apart is its intensity and its impact on daily life. For those with SAD, these feelings of dread are not just tied to one-off events but can be a recurring theme in many aspects of their life. This often leads to avoidance of social situations altogether. Further, it can lead to a cycle of isolation and missed opportunities, making it a challenging condition to navigate and overcome.
Techniques Used In Social Anxiety Counseling
In treating Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) and other anxiety-related conditions, therapists employ a range of evidence-based techniques designed to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Some of the most common techniques used in the context of social anxiety counseling include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
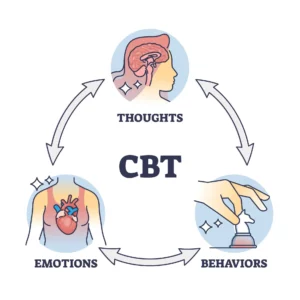
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a gold standard in the treatment of social anxiety. At its core, CBT focuses on the intertwined relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Within the scope of CBT:
- Cognitive Restructuring: This approach involves identifying negative, maladaptive thought patterns associated with social situations and challenging their validity. Patients learn to recognize these automatic thoughts and are taught techniques to reframe them into more positive or neutral ones.
- Behavioral Experiments: In this process, individuals are encouraged to test out the validity of their negative beliefs in controlled environments. Through these experiments, they can gather concrete evidence against their irrational fears.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is about confronting fears in a structured manner. For someone with SAD, this might mean progressively facing social situations they usually avoid. By repeatedly and gradually facing these situations, the emotional response of anxiety tends to diminish over time, reducing the power the fear has over the individual.
Systematic Desensitization
This therapeutic technique involves developing a hierarchy of anxiety-inducing situations. Starting with the least fear-provoking scenarios and pairing them with relaxation techniques, the patient gradually works their way up the hierarchy. This combination of exposure and relaxation allows for a gradual desensitization to the situations that induce anxiety.
Social Skills Training
Some individuals with SAD might lack certain social skills or feel insecure about their social competencies. Through role-playing, feedback sessions, and other interactive exercises, social skills training offers direct instruction and practice, focusing on areas like communication, assertiveness, and reading social cues.
Relaxation Techniques
Physical symptoms of anxiety can sometimes be overwhelming. Techniques such as:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Focus on controlled and mindful breathing. This can activate the body’s relaxation response.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This involves a two-step process of tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups. And, helping individuals understand the sensation of relaxation and apply it as needed.
- Guided Imagery: Engaging the mind with calming scenarios or images, guiding individuals away from the anxiety-inducing thoughts typical of SAD.
Mindfulness and Meditation
More than just a trend, mindfulness and meditation have shown profound effects on reducing anxiety. These practices teach individuals to stay present. And, allows them to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment, promoting a kinder and more compassionate internal dialogue.
Group Therapy
Group therapy offers a dual benefit for those with SAD. Firstly, it provides a safe and controlled environment for individuals to practice social interactions. Secondly, it provides a platform for peer feedback and support, allowing individuals to realize they’re not alone in their struggles.
Psychoeducation
Knowledge is power. By educating individuals about the nuances of SAD, its origins, and the science behind anxiety, patients can feel more in control and less intimated by their condition. Understanding the “why” behind their feelings often makes them more manageable.
Each person’s journey with social anxiety is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Hence, it’s vital to have a tailored approach, blending different techniques to find the most effective treatment plan.
What To Expect In A Counseling Session?
 Engaging in counseling, especially for the first time, can be both a hopeful and anxiety-inducing endeavor. Knowing what to expect can help alleviate some of the apprehension. Here’s a general overview of what typically occurs in a counseling session:
Engaging in counseling, especially for the first time, can be both a hopeful and anxiety-inducing endeavor. Knowing what to expect can help alleviate some of the apprehension. Here’s a general overview of what typically occurs in a counseling session:
1. Initial Intake and Assessment
The first session, often referred to as an intake or assessment, is primarily informational. The therapist will gather data about your background, present concerns, history of mental health, and any other relevant details. This session sets the groundwork for understanding the issues.
2. Establishing Rapport
One of the primary goals, especially in the initial sessions, is building a therapeutic alliance or rapport. It’s essential for the client to feel safe, understood, and respected. The therapist will likely employ active listening, empathy, and validation to foster this trust.
3. Goal Setting
Together, you and the therapist will identify specific goals for therapy. Whether it’s managing anxiety, improving relationships, or developing coping strategies, having clear objectives helps guide the therapeutic process.
4. Exploration and Insight
In subsequent sessions, you’ll delve deeper into your feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. This exploration provides insights into patterns, triggers, and underlying issues.
5. Skill Development
Depending on your goals and the therapeutic approach, a significant portion of sessions might focus on developing specific skills. This could include learning relaxation techniques, communication strategies, or cognitive reframing methods.
6. Feedback and Interaction
A counseling session is interactive. While you’ll be sharing your feelings and experiences, the therapist will provide feedback, and reflections, and sometimes challenge your perceptions to encourage growth and change.
7. Progress Evaluation
Periodically, the therapist will review your progress with you, discussing the strides made towards your goals and any adjustments needed in the treatment plan.
8. Closure and Termination
As therapy progresses and you near your goals, discussions about ending therapy will emerge. This phase involves reviewing the skills learned, progress made, and strategies for maintaining gains post-therapy. A proper closure ensures you feel empowered to move forward.
Most Importantly
- Confidentiality: It’s crucial to understand that, with a few exceptions (like harm to self or others), what you share in therapy remains confidential. This confidentiality is a cornerstone of the therapeutic relationship, ensuring you can speak openly and honestly.
- Logistics: Each session typically lasts between 45 to 60 minutes, though this can vary. The frequency of sessions will also fluctuate based on individual needs, with weekly sessions being the most common initially.
Lastly, it’s essential to remember that therapy is a collaborative process. While the therapist brings expertise in psychological theories and techniques, you are the expert on your life.
Pros And Cons Of Social Anxiety Counseling
Social anxiety counseling, like any therapeutic intervention, offers a variety of benefits as well as some potential drawbacks. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons:
Pros
- Deeper Understanding: Counseling provides insights into the root causes of social anxiety, helping individuals understand their triggers, patterns, and underlying beliefs.
- Safe Space: Therapy offers a judgment-free zone where individuals can openly discuss their fears, concerns, and experiences, providing both catharsis and validation.
- Professional Guidance: Working with a trained therapist ensures that individuals receive evidence-based interventions and expertise. This can be instrumental in promoting recovery.
- Holistic Growth: Beyond addressing social anxiety, counseling often leads to personal growth in various areas. Such as increased self-awareness, improved self-esteem, and better overall emotional well-being.
- Support and Validation: Interacting with a therapist can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide much-needed validation, reinforcing that one is not alone in their struggles.
Cons
- Financial Cost: While some insurance plans cover mental health services, therapy can be expensive. Especially if seeking services from specialists or attending multiple sessions per week.
- Emotional Discomfort: Delving into personal fears, past traumas, and deep-seated beliefs can be emotionally draining and sometimes exacerbate anxiety in the short term.
- Not Always Immediate Results: While some individuals might experience rapid improvements, therapy can be a slow process for others, requiring patience and persistence.
- Stigma: Despite advancements in mental health awareness, a stigma surrounding therapy still exists in some communities or cultures, which can deter individuals from seeking help.
- Relapse: Even after successful therapy, some individuals might experience relapses, especially during stressful periods or significant life changes.
While social anxiety counseling offers numerous benefits and has transformed many lives, it’s essential to consider both its advantages and potential drawbacks.
Finding The Right Social Anxiety Counselor Near Me
 The following are some strategies that can help you find the right counselor near you:
The following are some strategies that can help you find the right counselor near you:
- Ask for Referrals: Seek recommendations from primary care physicians, psychiatrists, or other healthcare professionals. Ask friends, family, or colleagues if they’ve had positive experiences with counselors.
- Check Qualifications and Expertise: Ensure the counselor is licensed in your state. Look for therapists who specialize in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or other evidence-based treatments for social anxiety.
- Consider Logistics: Check the therapist’s location, availability, and session times. Consider if they offer teletherapy or online sessions, especially if mobility or distance is a concern.
- Insurance and Payment: Confirm if the therapist accepts your insurance or if they offer a sliding scale based on income.
- Initial Consultation: Many therapists offer a free initial consultation (either in person, over the phone, or via video chat). Use this opportunity to gauge your comfort level with the therapist and ask any pertinent questions.
- Trust Your Instincts: After one or two sessions, reflect on your comfort level, the connection you felt, and whether you believe the therapist understands and can help with your specific concerns.
- Stay Updated: Regularly revisit your needs and assess the progress you’re making with your therapist. Open communication is key to ensuring the therapeutic process remains effective.
By following these steps and prioritizing your needs and comfort, you’ll be better equipped to find the right social anxiety counselor in your area.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex world of social anxiety can be a daunting journey, but with the right resources and professional guidance, relief and transformation are attainable. Whether you’re taking the first steps to understand social anxiety, weighing the pros and cons of counseling, or seeking the ideal therapist, remember you’re not alone in this journey. If you are experiencing anxiety-related issues, Online Anxiety Counseling in India at TherapyMantra can help: Book a trial Online therapy session


